GetClosedActivities
From Business Process Management, BPM and Workflow Automation Wiki | BizAgi BPMS
<keywords content="keywords"> getClosedActivities, getclosedactivities, getClosedActivitiesAsString, getclosedactivitiesasstring, get Closed Activities, get closed activities, SOA Layer, soa layer, WorkflowEngineSOA, workflowenginesoa, Workflow Engine SOA, workflow engine soa </keywords>
Contents |
getClosedActivities
A method from the WorkflowEngineSOA web service used to consult closed or finished activities in Bizagi from an external application. This document also applies to the getClosedActivitiesAsString method.
Description
This method receives an XML with the idCase (internal case identification number) for which the closed activities are required. The method getClosedActivities receives and returns an XmlDocument and getClosedActivitiesAsString receives and returns an XML in string format.
Input Data
Here is the schema of the expected XML (copy it from here):
Parameter 1 (XmlDocument or String Type)
BizAgiWSParam: Root node.
idCase: Activities belonging to this idCase (case identification number).
subprocessDepth: It is an indicator of subprocess’s depth. This is used when a Subprocess task type exists, to be able to retrieve activities in possible subprocesses for a case. By default, the query returns one level of depth, that is to say, the result will contain the activities of subprocesses related to the process of the actual case; but not activities of a subprocess’s subprocesses. It can be any integer but is important to keep in mind that for greater depth the query response time will increment, so, it is better to enter a small number.
Example
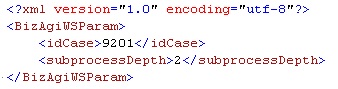
With the following XML the closed activities of case number 9201 will be returned. Since the sub-process depth is 2, also closed activities in a sub-process’s sub-process will be retrieved:
Output Data
The schema of the returned XML is as follows (copy it from here):
The response includes information of all closed activities matching the query. Here is the description of each data contained in the returned XML.
workItems: This is the root node of the response; it contains a "workItem" node for each activity included in the result.
workItem: This is a specific activity (an instance of a task) of the process that is active for a case.
workItemId: Identification number or key of the activity.
workItemState: State in which the activity is.
workItemEntryDate: Date and time when this activity was reached.
workItemDuration: Is the estimated duration, in minutes, for this activity.
workItemSubprocesses: If the activity is of a Subprocess type, this will contain information about the subprocess’s closed activities. It has a "workItems" child node so from here on the structure is like this same response including a "workItem" node for each activity matching the query in the subprocess.
workItemEstimatedSolutionDate: Is the activity’s estimated solution date.
workItemSolutionDate: The actual date in which the activity was completed.
task: Contains information about task corresponding to the activity.
taskId: Identification number or key of the task.
taskName: Name of the task.
taskDisplayName: Display name of the task.
taskDescription: Task’s descriptive text.
taskHelpText: Task’s help text.
HelpUrl: URL with information of the activity.
taskEstimatedDuration: Is the estimated duration, in minutes, for the task.
taskType: Type of task.
taskCost: The estimated cost of the task. This value, like the estimated dates, is configured and determined by the designer of the process.
taskPriority: Fulfillment priority of the task.
taskTransactional: An indicator stating if a task is transactional.
taskCompensation: States if this is a compensation task.
taskTimerEventDuration: If this is a timer task, it will contain its duration in minutes.
AllowsReassign: A mark showing if this task may be reassigned to another user.
SendNotification: Indicates if an email must be sent to a user informing of the availability of the task.
SendAlarms: Indicates if an email must be sent to the assigned user informing that the task is at risk of being overdue.
ExtendedEstimatedDuration: Estimated extended time duration.
Form: Reserved for future use.
IsAsynchTask: Specifies if this is an asynchronous task or not. Usually used for interfaces.
NumberOfRetries: Applies for asynchronous tasks. Is the number of automatic retries for the task in case it fails (an exception is thrown).
RetryInterval: Applies for asynchronous tasks. Is the time (in minutes) between each retry.
ShowFeedback: Applies for asynchronous tasks. Indicates if the user will be informed when an error occurs.
TimeoutSeconds: Applies for asynchronous tasks. Time (in seconds) the asynchronous task will wait for the external system to respond.
process: Has information about the process to which the activity belongs.
processId: Identification number of the case (idCase).
processCreationDate: Case creation date.
processSolutionDate: Case solution date.
processWorkflowClass: The information in this node is all about the process (process metadata) not about the particular case
workflowClassId: Identification number (or key) of the process.
workflowClassName: Name of the process.
workflowClassDisplayName: Display name of the process.
workflowClassDescription: Process description.
workflowClassHelpText: Process help text.
workflowClassHelpURL: Help URL for the process.
workflowClassDisplayOrder: The order in which the process will be viewed in the web application.
workflowClassCreationDate: Creation date of the process.
workflowClassGlobalForm: Identification number of the process’s global form (zero if it is not configured).
workflowClassAllocationPrinciple: Reserved for future use.
workflowClassProcessType: Process type.
workflowClassDisplay: Indicates whether the process is visible or not.
workflowClassUseParentRadicationNumber: Indicates if a case of this process uses its own creation number or the same number as the parent process (if it is a subprocess).
workflowClassSupportScopes: Indicates if the process supports Bizagi "scopes"; which is an efficient method of data persistence.
processError: Contains information of errors occurring during the processing of this method.
errorCode: Code of the error, if one occurred.
errorMessage: Message of the error, if one occurred.
Example
Here is the XML in response to the one send as example:
Go to SOA Layer <comments />