Business Policies
From Business Process Management, BPM and Workflow Automation Wiki | BizAgi BPMS
<keywords content="keywords"> conditions, condition, define rule, table, chart, definition, policy, policies </keywords>
Business Rules (Business Policies)
Policies allow an organization to adapt itself to business changes which are controlled with agility and flexibility by rules. Policies promote the autonomy of the process owners, so that they can be involved in the control of the rules defined by the organization. The rules are applied according to the business and market conditions and they define how the cases must be handled.
Business rules can be changed at any time from the Web application. Changes in values or logic can be made but new rules cannot be created in the Web application.
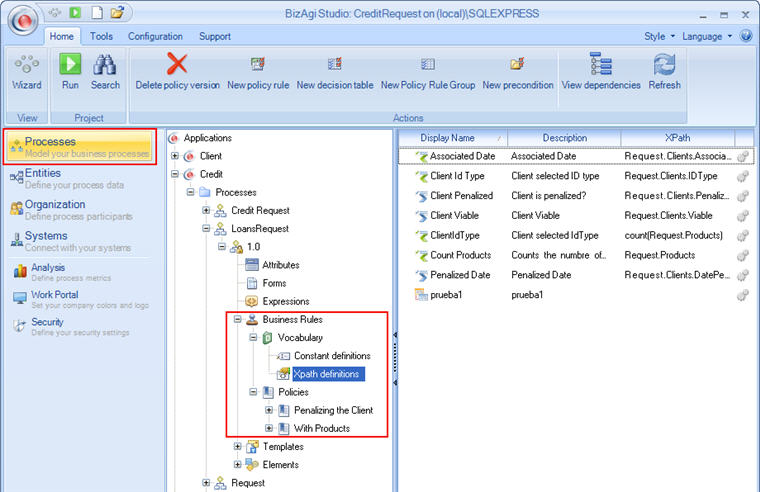
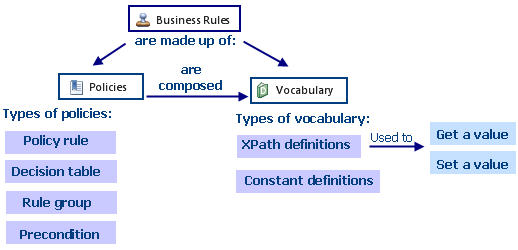
It is very important to understand that Business Rules are composed of Policies, and Policies are composed of Vocabulary.
Initial considerations
![]() Business Rules refer to the rules or rule groups that evaluate conditions to define actions or results.
Business Rules refer to the rules or rule groups that evaluate conditions to define actions or results.
![]() Business rules are found in the Bizagi Processes menu (i.e. they can only be used in the process where they were created).
Business rules are found in the Bizagi Processes menu (i.e. they can only be used in the process where they were created).
![]() Policies include policy rules, decision tables, groups of rules and preconditions (decision trees). A policy can also contain one or several of these elements and combinations of them; for example, three policy rules or one policy rule and one decision table.
Policies include policy rules, decision tables, groups of rules and preconditions (decision trees). A policy can also contain one or several of these elements and combinations of them; for example, three policy rules or one policy rule and one decision table.
![]() The vocabulary must be generated before the business policy can be generated.
The vocabulary must be generated before the business policy can be generated.
![]() Vocabulary can be used to evaluate and obtain values:
Vocabulary can be used to evaluate and obtain values:
- It can be constant, for example, the value of the minimum monthly legal wage. The administration module includes this value; it is not an attribute of the business data model.
- The vocabulary can also be an XPath definition, which is the value of an attribute of the data model.
- The attribute value can also contain the result of a table operation such as sum, average, maximum, minimum, and count; for example, the sum of the required values for the case’s products or the request application’s date.
![]() Vocabulary can be used to assign values:
Vocabulary can be used to assign values:
- To assign values the vocabulary must be an XPath Definition. For example, the state of a request (approved, rejected).
Related Articles
<comments />