Expressions
From Business Process Management, BPM and Workflow Automation Wiki | BizAgi BPMS
<keywords content="keywords">rule, Xpath, Expression, Expressions, What is a rule, event, assign, Event, events, Action, actions, visibility, required, edit, condition, conditions</keywords>
Contents |
Expressions
In order to achieve the goals that have been proposed, today companies define special norms or policies that must be fulfilled in certain activities of the daily processes of the organization. It is common to see that these special conditions or exceptions vary in accordance with the demands of the changing environment.
Bizagi is capable of continuously and dynamically define, verify, and modify a large number of conditions or policies (simple or complex), in accordance with the organization’s demands.
This section of the manual gives a detailed definition of each type of Expression rules that can be defined and created using Bizagi. In addition, there is a step-by-step guide on how to create from the most simple to the most complex Expression rules.
Expression Rules
Expression Rules in Bizagi are the conditions, validations and norms that must be satisfied and controlled within the organization, defined in accordance with the organization’s expected business performance. Expression rules are a fundamental component of Bizagi.
All expressions use Xpath navigation, which is a mechanism to standardize the language in the tool and makes handling business rules more intuitive for everyone involved. It is very important that before using Expressions, the Xpath concept is understood.
Expressions are associated directly with the processes, that is, they correspond to the rules of transition, assignment, actions or conditions of visibility, mandatory nature or editing of attributes within the forms.
In addition, rules can call upon any Function defined in Bizagi.
![]() How to Create an Expression Rule
How to Create an Expression Rule
Uses of Expression Rules
The use of Expression Rules can be classified into five groups, as follows:
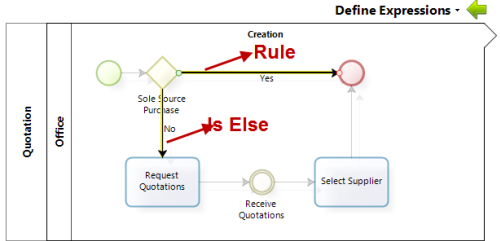
![]() Expressions associated with Sequence Flows: this expressions are the rules that allow you to verify whether a specific condition is being met at a certain point in the process and the process continues on the path associated with the condition that was met. These rules should always result in true or false and they are associated with the following shapes:
Expressions associated with Sequence Flows: this expressions are the rules that allow you to verify whether a specific condition is being met at a certain point in the process and the process continues on the path associated with the condition that was met. These rules should always result in true or false and they are associated with the following shapes:
![]() Exclusive Gateway (divergence element)
Exclusive Gateway (divergence element)
![]() Inclusive Gateway (divergence element)
Inclusive Gateway (divergence element)
![]() Expressions for fields to be or not: visibile, editable and required: These rules are used to validate information. That is, they make sure the information is saved properly for the execution of the process, allowing to make an attribute visible, required or editable in a form in accordance with a condition (there is another way to do this that is not handled using these rules but by the options of Behaviours and Actions available for each attribute in the form editor).
Expressions for fields to be or not: visibile, editable and required: These rules are used to validate information. That is, they make sure the information is saved properly for the execution of the process, allowing to make an attribute visible, required or editable in a form in accordance with a condition (there is another way to do this that is not handled using these rules but by the options of Behaviours and Actions available for each attribute in the form editor).
As in the case for the rules of transition, they have the characteristic that they should result in true or false (in other words they have to be boolean). In order to associate these rules, use the form modeler to follow these steps:
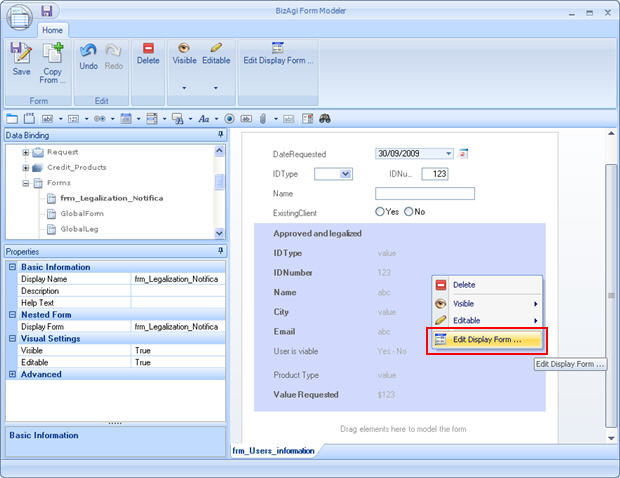
![]() If the field the user is going to modify is in a nested form, first right click on the field and select Edit Display Form
If the field the user is going to modify is in a nested form, first right click on the field and select Edit Display Form
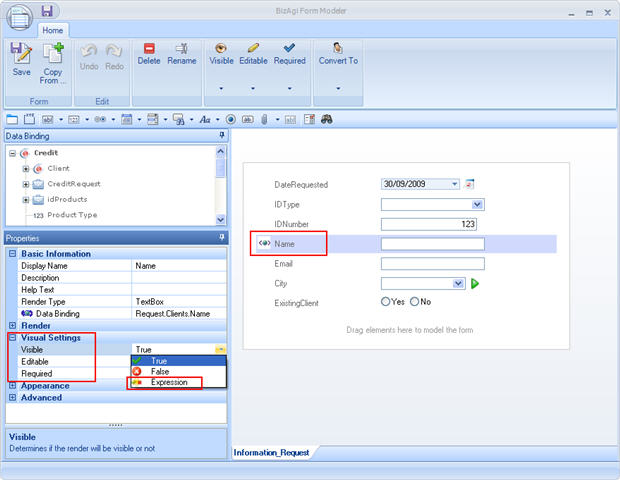
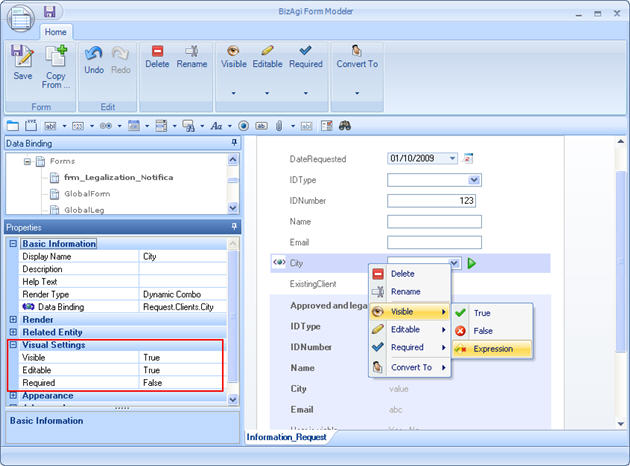
![]() Select the field where the rule is going to be added in its visual settings. Right click on the field and select the property (visible, editable, or required) and then click on Rule.
Select the field where the rule is going to be added in its visual settings. Right click on the field and select the property (visible, editable, or required) and then click on Rule.
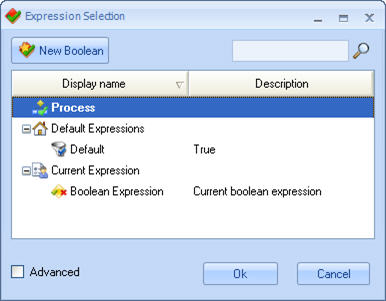
![]() The Expression Selection window will open for the user to select the rule (if it was already created) or to create the rule by clicking on the New Boolean button.
The Expression Selection window will open for the user to select the rule (if it was already created) or to create the rule by clicking on the New Boolean button.
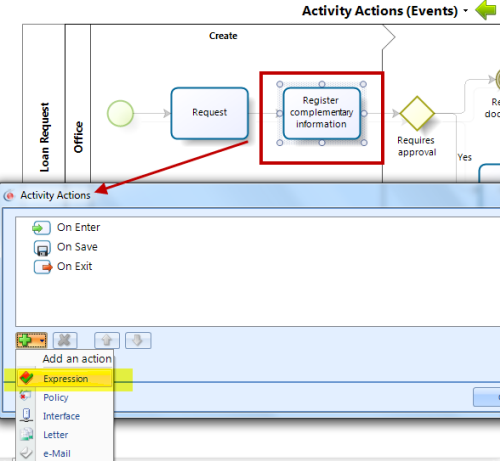
![]() Expressions used in Actions (Events) within a shape:These rules allow the execution of an action at the beginning, on saving or on exiting an activity. (On enter, on save, or on exit)
Expressions used in Actions (Events) within a shape:These rules allow the execution of an action at the beginning, on saving or on exiting an activity. (On enter, on save, or on exit)
Examples:
![]() Add or delete records from a Table
Add or delete records from a Table
![]() Call on components, Interfaces, WebServices
Call on components, Interfaces, WebServices
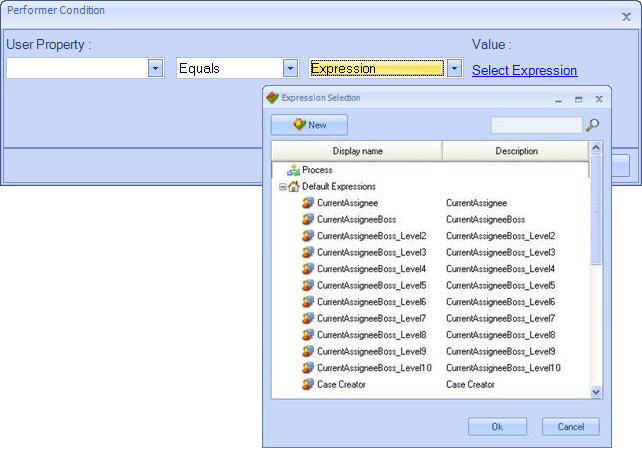
![]() Expressions to Assign Activities: Assignments have two rules. One that determines the condition to carry out the assignment and the other to determine the specific user that should carry out the activity.
Expressions to Assign Activities: Assignments have two rules. One that determines the condition to carry out the assignment and the other to determine the specific user that should carry out the activity.
The rules that determine the condition to carry out the assignment always return true or false. In addition, the rules of assignment determine the specific profile (location, area, position, role and/or skill) or user who should carry out the activity within the process.
Expression type
There are four types of expressions that are used according to the place where they are called upon and the user's needs.
![]() Boolean: These are all the rules that return True or False. The rules that belong to this category can be used in:
Boolean: These are all the rules that return True or False. The rules that belong to this category can be used in:
![]() Expressions associated with sequence flows
Expressions associated with sequence flows
![]() Expressions used as conditions for attributes (fields in the forms) to be (or not) visible, editable or required.
Expressions used as conditions for attributes (fields in the forms) to be (or not) visible, editable or required.
![]() Expressions used to determine the condition to assign an activity.
Expressions used to determine the condition to assign an activity.
Example: When the user associates a transition expression (in an exclusive or inclusive gateway), in the list of rules to select, the user can only see the rules that have been cataloged as Boolean. The user will also be able to create New Boolean.
![]() User: These are the rules used for assignations and should return an Array List with a collection of user properties. These are used for assignations. In other words, they return one or more idUsers, one or more idLocations, idPositions, idSkills, idRoles, idAreas or any other user property used for assignation.
User: These are the rules used for assignations and should return an Array List with a collection of user properties. These are used for assignations. In other words, they return one or more idUsers, one or more idLocations, idPositions, idSkills, idRoles, idAreas or any other user property used for assignation.
These rules can also be associated as Actions of the shapes in a process.
Example : When associating an assignation rule, in the list of available rules, only the rules with expression type Users will be visualized by the user.
![]() Scripting: Any rule that do not fall into the categories mentioned above are known as code rules. These rules can carry out any type of task and they do not have to return any type of data in particular. The rules that belong to this category can be used in:
Scripting: Any rule that do not fall into the categories mentioned above are known as code rules. These rules can carry out any type of task and they do not have to return any type of data in particular. The rules that belong to this category can be used in:
![]() Scripting boolean: These are code rules (just like the Scripting expressions) that must return True or False. Scripting booleans are advanced boolean expressions because sometimes regular booelans are not enough for what is desired, and need some code writting before the returning value.
Scripting boolean: These are code rules (just like the Scripting expressions) that must return True or False. Scripting booleans are advanced boolean expressions because sometimes regular booelans are not enough for what is desired, and need some code writting before the returning value.
![]() Expressions associated with transitions
Expressions associated with transitions
![]() Expressions used as conditions for attributes (fields in the forms) to be (or not) visible, editable or required.
Expressions used as conditions for attributes (fields in the forms) to be (or not) visible, editable or required.
![]() Expressions used to determine the condition to assign an activity.
Expressions used to determine the condition to assign an activity.
Expressions in Production
When a project has been deployed, some elements like Expressions will have some restrictions to avoid possible problems with subsequent deployments. For this reason, when an Expression is already in production it will not be possible to delete it and a warning message will be displayed when a user changes its code.
Related Information
| Task | Description |
|
Manage Expressions |
|
|
Different ways to create an expression | |
|
Several ways to associate an expression to a process | |
|
Classification of Expression according to the Reusability | |
|
Types of Modules in the Expressions | |
|
Examples of some advanced Functions .Me | |
|
Explanation of Iterate Over Xpath and its usability | |
|
Some recommendations when creating Business Rules | |
|
Xpath |
|
|
Some of the main Xpath functions in Expressions | |
|
How to Build Xpath Expressions | |
|
Set and Get information in Expressions using Xpath | |
|
Common Operations |
|
|
Examples of Date operations in Expressions | |
|
Examples of String operations in Expressions | |
|
How to Filter information | |
|
Make comparissons with Null in Expressions | |
|
Explanation of the main Mathematical functions available in Expressions | |
|
How to send Mails from Expressions | |
|
Types of Expressions |
|
|
Expressions with Global Scope | |
|
Expressions with Application Scope | |
|
Expressions with Process Scope | |
|
Expressions with Entity Scope | |
|
Default Expressions in Bizagi | |
|
Functions in Bizagi | |
|
How to group Expressions in Bizagi by families |
<comments />